Anodising is a non-contact mechanical passivation process used in the production of aluminium alloys and other metals with high carbon content. It involves passing an electric current through the part whilst the part is hot, which is subsequently converted into heat. This process is known as ‘thermal anodising’. The process helps to remove impurities such as excess moisture, carbon dust and soluble contaminants such as zinc and sulphur from the surface of the component in question. Anodising is used for several applications in the aerospace industry, including the manufacture of aluminium alloys, parts for electric components, propellers and many others. One of the most prominent providers of this service is Poeton.
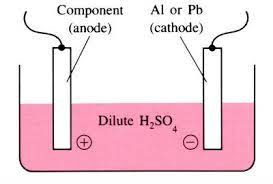
There are two different types of anodising, soft and hard anodising. Soft anodising is done with the help of water or by passing a pulse of water through the component, whilst the hard type of anodizing is done with the help of a chemical. Depending on your application you will need to know what type of anodising is required for your project. In general soft anodising is preferred over hard anodising because of its availability in a range of conditions, including low temperatures and pressure, as well as its ability to be performed at relatively low cost.
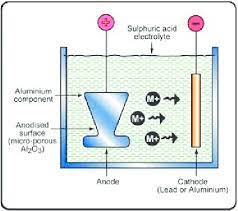
For some applications, particularly where the component being formed is small in size, the use of hard anodising is preferred. This is because it creates a thicker oxide layer and results in a larger component that can withstand higher stress levels. Examples of this type of component are door seals, pump seals and exhaust pipes. Another example is where the component to be formed is thin (thin sheets of aluminium) so that the application requires a thicker oxide layer to prevent corrosion occurring.